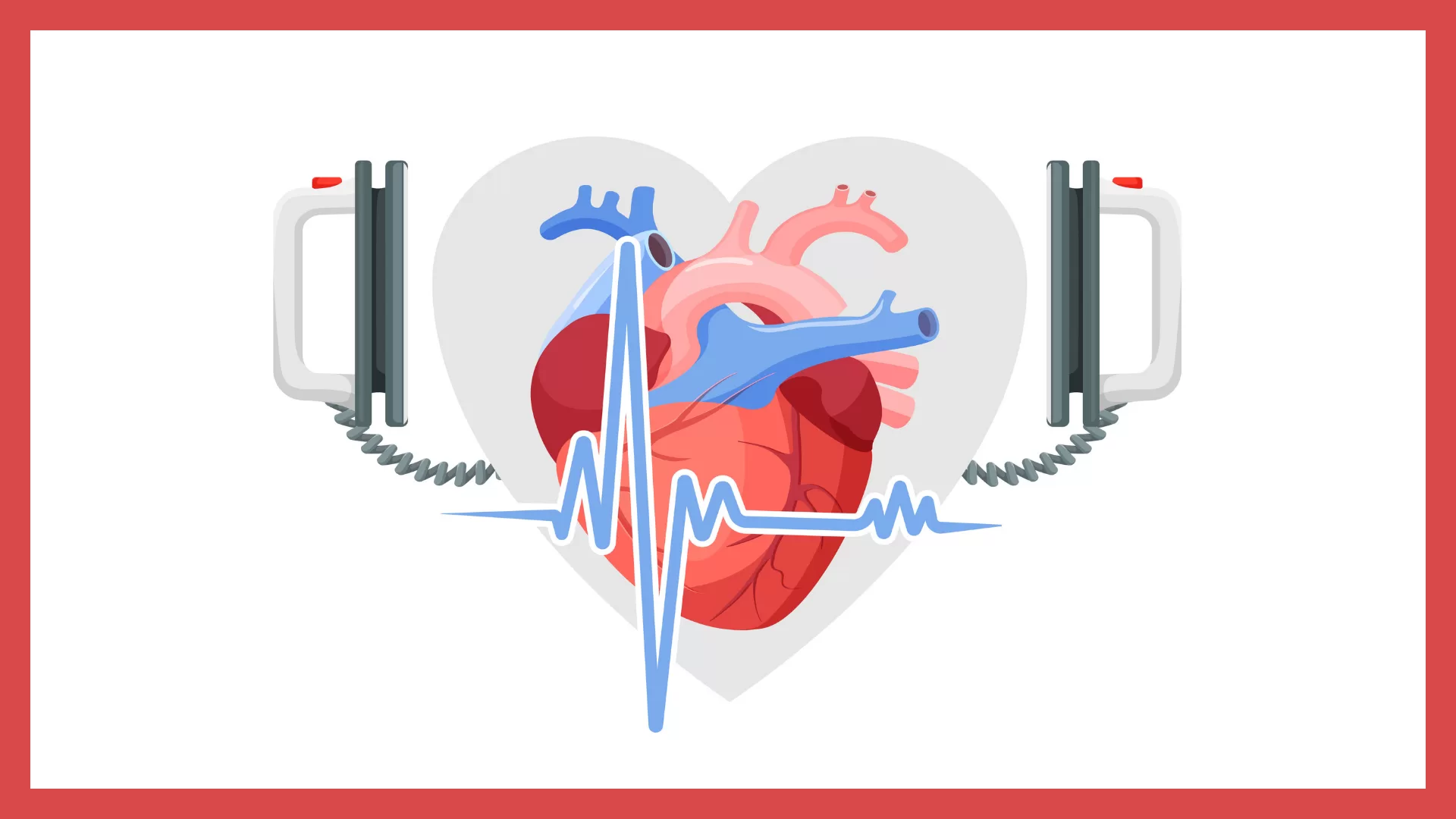
Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency that occurs suddenly when the heart stops pumping blood to the body. This can happen due to various reasons such as heart disease, heart attack, electric shock, drowning, or drug overdose. Cardiac arrest can happen to anyone, at any time, regardless of age or gender.
Recognizing the symptoms of cardiac arrest is crucial, as it can help in administering prompt and effective medical care. Here are some common symptoms of cardiac arrest to look out for:
1. Sudden loss of consciousness:
The person may lose consciousness suddenly without any warning signs.
2. Absence of pulse:
The person will not have a pulse, and their breathing will be irregular.
3. No breathing or gasping:
The person will not be able to breathe or will gasp for air.
4. Chest pain:
The person may experience chest pain or discomfort before collapsing.
5. Dizziness or lightheadedness:
The person may feel dizzy or lightheaded before collapsing.
The person may experience nausea or vomiting.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, call for medical assistance immediately. Prompt medical attention is crucial in case of cardiac arrest, as it can increase the chances of survival.
There are some factors that increase the risk of cardiac arrest, including:
– Age over 45 years
– Family history of heart disease
– Smoking
– High blood pressure
– High cholesterol
– Diabetes
– Obesity
– Sedentary lifestyle
– Drug or alcohol abuse
It is important to keep in mind that not all cardiac arrests are preventable, but we can reduce the risk by implementing lifestyle changes. These include following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and managing health conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
In conclusion, cardiac arrest can be a life-threatening emergency, and recognizing the symptoms plays a crucial role in saving lives. If you or a loved one experience any of the above symptoms, call for medical assistance immediately. Also, ensure to make healthy lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of cardiac arrest.